Using the Vercel AI SDK with Gram-hosted MCP servers
The Vercel AI SDK supports remote MCP servers through its experimental MCP client feature. This allows you to give AI models direct access to your tools and APIs by connecting to Gram-hosted MCP servers.
This guide shows you how to connect the Vercel AI SDK to a Gram-hosted MCP server using an example Push Advisor API. You’ll learn how to create an MCP server from an OpenAPI document, set up the connection, configure authentication, and use natural language to query the example API.
Find the full code and OpenAPI document in the Push Advisor API repository.
Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”You’ll need:
- A Gram account
- An OpenAI API key or Anthropic API key
- A Node.js environment set up on your machine
- Basic familiarity with TypeScript, JavaScript, and making API requests
Creating a Gram MCP server
Section titled “Creating a Gram MCP server”If you already have a Gram MCP server configured, you can skip to connecting the Vercel AI SDK to your Gram-hosted MCP server. For an in-depth guide to how Gram works and to creating a Gram-hosted MCP server, check out our introduction to Gram.
Setting up a new Gram project
Section titled “Setting up a new Gram project”In the Gram dashboard, click New Project to start the guided setup flow for creating a toolset and MCP server.
When prompted, upload the Push Advisor OpenAPI document.
Follow the steps to configure a toolset and publish an MCP server. At the end of the setup, you’ll have a Gram-hosted MCP server ready to use.
For this guide, we’ll use the public server URL https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod.
For authenticated servers, you’ll need an API key. Generate an API key in the Settings tab.
Connecting the Vercel AI SDK to your Gram-hosted MCP server
Section titled “Connecting the Vercel AI SDK to your Gram-hosted MCP server”The Vercel AI SDK supports MCP servers through the experimental_createMCPClient function with Streamable HTTP transport. Here’s how to connect to your Gram-hosted MCP server:
Installation and setup
Section titled “Installation and setup”First, install the Vercel AI SDK, the MCP SDK, and an AI provider SDK. The samples in this guide use OpenAI, but you can also use Anthropic or other providers.
Run the following:
npm install ai @ai-sdk/openai @modelcontextprotocol/sdk dotenv# if using Anthropic, add# npm install @ai-sdk/anthropicProject configuration
Section titled “Project configuration”Configure your project for ES modules by adding "type": "module" to your package.json:
{ "name": "my-gram-integration", "version": "1.0.0", "type": "module", "main": "index.js", "dependencies": { "ai": "^5.0.21", "@ai-sdk/openai": "^2.0.19", "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk": "^1.17.3", "dotenv": "^16.0.0" }}Environment variables
Section titled “Environment variables”Create a .env file in your project root to store your API keys:
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-api-key-hereANTHROPIC_API_KEY=your-anthropic-api-key-here # if using AnthropicGRAM_API_KEY=your-gram-api-key-here # for authenticated Gram serversLoad these environment variables at the top of your JavaScript files:
import dotenv from 'dotenv';dotenv.config();Basic connection (public server)
Section titled “Basic connection (public server)”Here’s a basic example using a public Gram MCP server with Streamable HTTP transport:
import { experimental_createMCPClient as createMCPClient } from 'ai';import { StreamableHTTPClientTransport } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/streamableHttp.js';import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';import { streamText } from 'ai';import { stepCountIs } from 'ai';import dotenv from 'dotenv';
// Load environment variablesdotenv.config();
// Create HTTP transport for your Gram-hosted MCP serverconst httpTransport = new StreamableHTTPClientTransport( new URL('https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod'));
// Create an MCP client using the Streamable HTTP transportconst mcpClient = await createMCPClient({ transport: httpTransport,});
// Get tools from the MCP serverconst tools = await mcpClient.tools();
// Use the tools with AI SDKconst result = await streamText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), tools, prompt: "Can I push to production today? Please check the status.", stopWhen: stepCountIs(2), // Ensure text response after tool call onStepFinish: ({ toolCalls, toolResults }) => { // Log tool calls as they complete toolCalls?.forEach(call => { console.log(`🔧 Called tool: ${call.toolName}`); });
toolResults?.forEach(result => { console.log(`📊 Tool result: ${JSON.stringify(result.output)}`); }); }, onFinish: async () => { await mcpClient.close(); },});
// Print the responseconsole.log('AI Response:');for await (const textPart of result.textStream) { process.stdout.write(textPart);}Authenticated connection
Section titled “Authenticated connection”For authenticated Gram MCP servers, include your Gram API key in the headers:
import { experimental_createMCPClient as createMCPClient } from 'ai';import { StreamableHTTPClientTransport } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/streamableHttp.js';import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';import { generateText } from 'ai';import { stepCountIs } from 'ai';import dotenv from 'dotenv';
// Load environment variablesdotenv.config();
const GRAM_API_KEY = process.env.GRAM_API_KEY;
if (!GRAM_API_KEY) { throw new Error('Missing GRAM_API_KEY environment variable');}
// Create HTTP transport with authenticationconst httpTransport = new StreamableHTTPClientTransport( new URL('https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod'), { headers: { Authorization: `Bearer ${GRAM_API_KEY}`, }, });
let mcpClient;
try { // Create an authenticated MCP client mcpClient = await createMCPClient({ transport: httpTransport, });
const tools = await mcpClient.tools();
const { text, toolCalls, toolResults } = await generateText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), tools, prompt: 'Can I push to production today?', stopWhen: stepCountIs(2), // Ensure text response after tool call });
// Access tool call information if (toolCalls && toolCalls.length > 0) { console.log('Tool calls made:'); toolCalls.forEach(call => { console.log(`- Called tool: ${call.toolName}`); console.log(`- With args: ${JSON.stringify(call.input)}`); }); }
// Access tool results if (toolResults && toolResults.length > 0) { console.log('Tool results:'); toolResults.forEach(result => { console.log(`- Tool result: ${JSON.stringify(result.output)}`); }); }
console.log(`Final response: ${text}`);} finally { if (mcpClient) { await mcpClient.close(); }}Understanding the configuration
Section titled “Understanding the configuration”Here’s what each parameter in the createMCPClient configuration does:
StreamableHTTPClientTransportuses Streamable HTTP transport (as opposed to SSE or stdio).new URL(...)adds your Gram-hosted MCP server URL.headersadds optional HTTP headers for authentication (passed as the second parameter to the transport constructor).
Tool filtering and schema approaches
Section titled “Tool filtering and schema approaches”The Vercel AI SDK supports two approaches to working with MCP tools: schema discovery and schema definition.
Schema discovery (recommended for Gram)
Section titled “Schema discovery (recommended for Gram)”Schema discovery is the simplest approach, where all tools offered by the server are listed automatically:
// Discover all tools from the serverconst tools = await mcpClient.tools();
// All tools are now available for useconst result = await generateText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), tools, prompt: 'Is it safe to deploy today?',});Schema definition with TypeScript
Section titled “Schema definition with TypeScript”For better type safety and IDE support, you can define schemas explicitly:
import { z } from 'zod';
// Define specific tools with their schemasconst tools = await mcpClient.tools({ schemas: { 'can_i_push_to_prod': { inputSchema: z.object({}), }, 'vibe_check': { inputSchema: z.object({}), }, },});
// Now only the specified tools are availableconst result = await generateText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), tools, prompt: 'What is the vibe today?',});When you define schemas, the client only pulls the explicitly defined tools, even if the server offers additional tools.
Limiting tools with activeTools
Section titled “Limiting tools with activeTools”You can also limit which tools are available to the model using the activeTools parameter:
const tools = await mcpClient.tools();
const result = await generateText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), tools, activeTools: ['can_i_push_to_prod'], // Only this tool is available prompt: 'What is the vibe today?',});Working with responses
Section titled “Working with responses”The Vercel AI SDK provides different ways to handle MCP tool calls depending on whether you use generateText or streamText.
Using generateText
Section titled “Using generateText”With generateText, you get access to tool calls and results in the response:
// Create HTTP transport for Gram MCP serverconst httpTransport = new StreamableHTTPClientTransport( new URL('https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod'));
const mcpClient = await createMCPClient({ transport: httpTransport,});
try { const tools = await mcpClient.tools();
const { text, toolCalls, toolResults } = await generateText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), tools, prompt: 'Can I push to production today?', });
// Access tool call information toolCalls.forEach(call => { console.log(`Called tool: ${call.toolName}`); console.log(`With args: ${JSON.stringify(call.input)}`); });
// Access tool results toolResults.forEach(result => { console.log(`Tool result: ${JSON.stringify(result.output)}`); });
console.log(`Final response: ${text}`);} finally { await mcpClient.close();}Using streamText
Section titled “Using streamText”With streamText, you can handle tool calls as they stream in:
// Create HTTP transport for Gram MCP serverconst httpTransport = new StreamableHTTPClientTransport( new URL('https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod'));
const mcpClient = await createMCPClient({ transport: httpTransport,});
const tools = await mcpClient.tools();
const result = await streamText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), tools, prompt: 'What is the deployment status?', onStepFinish: ({ toolCalls, toolResults }) => { // Handle tool calls as they complete toolCalls?.forEach(call => { console.log(`Tool called: ${call.toolName}`); });
toolResults?.forEach(result => { console.log(`Tool result: ${JSON.stringify(result.output)}`); }); }, onFinish: async ({ text, toolCalls, toolResults }) => { console.log(`Final text: ${text}`); console.log(`Total tool calls: ${toolCalls.length}`); await mcpClient.close(); },});
// Stream the text responsefor await (const textPart of result.textStream) { process.stdout.write(textPart);}Error handling
Section titled “Error handling”The Vercel AI SDK includes error handling for MCP tool calls:
Connection errors
Section titled “Connection errors”Handle MCP client connection failures:
import { experimental_createMCPClient as createMCPClient } from 'ai';import { StreamableHTTPClientTransport } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/streamableHttp.js';
let mcpClient;
try { const httpTransport = new StreamableHTTPClientTransport( new URL('https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod'), { headers: { Authorization: `Bearer ${GRAM_API_KEY}`, }, } );
mcpClient = await createMCPClient({ transport: httpTransport, });
const tools = await mcpClient.tools(); // Use tools...} catch (error) { console.error('Failed to connect to MCP server:', error); // Fallback logic or error handling} finally { if (mcpClient) { await mcpClient.close(); }}Tool execution errors
Section titled “Tool execution errors”Handle errors that occur during tool execution:
import { generateText } from 'ai';import { stepCountIs } from 'ai';
let mcpClient;
try { // ... MCP client setup ...
const result = await generateText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), tools, prompt: 'Deploy to production', stopWhen: stepCountIs(2), onStepFinish: ({ toolResults }) => { // Check for tool errors in the results toolResults?.forEach(result => { if (result.type === 'tool-result' && result.output.isError) { console.error(`Tool error in ${result.toolName}:`, result.output); } else if (result.type === 'tool-result') { console.log(`Tool ${result.toolName} executed successfully`); } }); }, });
// Also check for errors in the final steps result.steps.forEach(step => { step.content.forEach(content => { if (content.type === 'tool-error') { console.error(`Tool error: ${content.error}`); console.error(`Tool name: ${content.toolName}`); } }); });} catch (error) { console.error('Generation error:', error);} finally { if (mcpClient) { await mcpClient.close(); }}For more advanced error handling patterns and troubleshooting, consult the Vercel AI SDK GitHub repository.
Generating text responses with tool calls
Section titled “Generating text responses with tool calls”Important: By default, generateText() stops after executing tools and may return empty text responses. To get text responses after tool calls, you need to use multi-step generation.
Understanding the default behavior
Section titled “Understanding the default behavior”When using tools with generateText(), the default behavior is as follows:
- The model calls the appropriate tool(s).
- The model receives tool results.
- The model stops without generating a text response.
This is by design - some tool calls are meant to be fire-and-forget operations that don’t require text responses.
Getting text responses after tool calls
Section titled “Getting text responses after tool calls”To generate text responses after tool calls, use stopWhen: stepCountIs(N), where N ≥ 2:
import { stepCountIs } from 'ai';
const result = await generateText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), tools, prompt: 'Can I push to production today?', stopWhen: stepCountIs(2), // Minimum: 1 step for tool call + 1 step for response});
console.log(result.text);This forces the model to:
- Step 1: Execute tool calls
- Step 2: Generate text response based on tool results
Multi-step tool calls
Section titled “Multi-step tool calls”For complex workflows requiring multiple tools and responses, use higher step counts:
import { stepCountIs } from 'ai';
let mcpClient;
try { // Create HTTP transport for Gram MCP server const httpTransport = new StreamableHTTPClientTransport( new URL('https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod') );
mcpClient = await createMCPClient({ transport: httpTransport, });
const tools = await mcpClient.tools();
const { text, steps } = await generateText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), tools, stopWhen: stepCountIs(5), // Stop after 5 steps if tools were called prompt: 'Check if I can deploy and then tell me the vibe', onStepFinish: ({ text, toolCalls, toolResults }) => { console.log(`Step completed with ${toolCalls.length} tool calls`); if (text) { console.log(`Step text: ${text}`); } }, });
// Access all tool calls from all steps const allToolCalls = steps.flatMap(step => step.toolCalls); console.log(`Total tool calls across all steps: ${allToolCalls.length}`); console.log(`Final response: ${text}`);} finally { if (mcpClient) { await mcpClient.close(); }}Client lifecycle management
Section titled “Client lifecycle management”Proper management of the MCP client lifecycle is important for resource efficiency:
Short-lived usage (recommended)
Section titled “Short-lived usage (recommended)”For single requests or short-lived operations, close the client when finished:
let mcpClient;
try { // Create HTTP transport for Gram MCP server const httpTransport = new StreamableHTTPClientTransport( new URL('https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod') );
mcpClient = await createMCPClient({ transport: httpTransport, });
const tools = await mcpClient.tools(); const result = await generateText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), tools, prompt: 'Your prompt here', }); // Process result...} finally { if (mcpClient) { await mcpClient.close(); }}Long-running applications
Section titled “Long-running applications”For server applications or CLI tools, you might keep the client open:
// Initialize once at startuplet mcpClient;
async function initializeMCPClient() { const httpTransport = new StreamableHTTPClientTransport( new URL('https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod') );
mcpClient = await createMCPClient({ transport: httpTransport, });}
// Clean up on application shutdownprocess.on('SIGINT', async () => { if (mcpClient) { await mcpClient.close(); process.exit(0); }});Differences from other MCP integrations
Section titled “Differences from other MCP integrations”The Vercel AI SDK’s approach to MCP differs from OpenAI and Anthropic’s native implementations:
Connection method
Section titled “Connection method”- The Vercel AI SDK uses
experimental_createMCPClientwith Streamable HTTP or stdio transports. - OpenAI uses the
toolsarray withtype: "mcp"in the Responses API. - Anthropic uses the
mcp_serversparameter in the Messages API.
Authentication
Section titled “Authentication”- The Vercel AI SDK uses HTTP headers in the transport configuration.
- OpenAI uses a headers object in the tool configuration.
- Anthropic uses an authorization token parameter.
Tool management
Section titled “Tool management”- The Vercel AI SDK allows schema discovery and definition at the client level and uses
activeToolsfor filtering. - OpenAI allows tool filtering via
allowed_toolsparameter. - Anthropic uses a tool configuration object with an
allowed_toolsarray.
Model flexibility
Section titled “Model flexibility”- The Vercel AI SDK works with any AI provider (including OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google).
- OpenAI only works with OpenAI models.
- Anthropic only works with Anthropic models.
Transport options
Section titled “Transport options”- The Vercel AI SDK uses Streamable HTTP, stdio, or custom transports.
- OpenAI uses direct HTTP or HTTPS connections.
- Anthropic uses URL-based HTTP connections.
Response handling
Section titled “Response handling”- The Vercel AI SDK handles responses via unified tool calls and results across all providers.
- OpenAI handles responses via the
mcp_callandmcp_list_toolsitems. - Anthropic handles responses via the
mcp_tool_useandmcp_tool_resultblocks.
Complete example
Section titled “Complete example”Here’s a complete example that demonstrates connecting to a Gram MCP server and using it with the Vercel AI SDK:
import { experimental_createMCPClient as createMCPClient } from 'ai';import { StreamableHTTPClientTransport } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/streamableHttp.js';import { openai } from '@ai-sdk/openai';import { streamText } from 'ai';
async function main() { // Set up environment variables const GRAM_API_KEY = process.env.GRAM_API_KEY; const OPENAI_API_KEY = process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY;
if (!GRAM_API_KEY || !OPENAI_API_KEY) { throw new Error('Missing required API keys'); }
let mcpClient;
try { // Create HTTP transport with authentication const httpTransport = new StreamableHTTPClientTransport( new URL('https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod'), { headers: { Authorization: `Bearer ${GRAM_API_KEY}`, }, } );
// Create MCP client with authentication mcpClient = await createMCPClient({ transport: httpTransport, });
// Get tools from the MCP server const tools = await mcpClient.tools(); console.log(`Connected to MCP server with ${Object.keys(tools).length} tools`);
// Stream a response using the tools const result = await streamText({ model: openai('gpt-4o'), tools, prompt: 'Can I push to production today, and what is the vibe?', onStepFinish: ({ toolCalls, toolResults }) => { // Log tool usage toolCalls?.forEach(call => { console.log(`\n🔧 Called tool: ${call.toolName}`); });
toolResults?.forEach(result => { console.log(`📊 Result: ${JSON.stringify(result.output)}`); }); }, });
// Stream the response to console console.log('\n💬 AI Response:'); for await (const textPart of result.textStream) { process.stdout.write(textPart); } console.log('\n');
} catch (error) { console.error('Error:', error); } finally { // Always close the MCP client if (mcpClient) { await mcpClient.close(); console.log('MCP client closed'); } }}
// Run the examplemain().catch(console.error);Testing your integration
Section titled “Testing your integration”If you encounter issues during integration, follow these steps to troubleshoot:
Validate MCP server connectivity
Section titled “Validate MCP server connectivity”Before integrating into your application, test your Gram MCP server in the Gram Playground to ensure the tools work correctly.
Use the MCP Inspector
Section titled “Use the MCP Inspector”Anthropic provides an MCP Inspector command line tool that helps you test and debug MCP servers before integrating them with the Vercel AI SDK. You can use it to validate your Gram MCP server’s connectivity and functionality.
Run the command below to test your Gram MCP server with the Inspector:
# Install and run the MCP Inspectornpx -y @modelcontextprotocol/inspectorIn the Transport Type field, select Streamable HTTP.
Enter your server URL in the URL field, for example:
https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprodClick Connect to establish a connection to your MCP server.
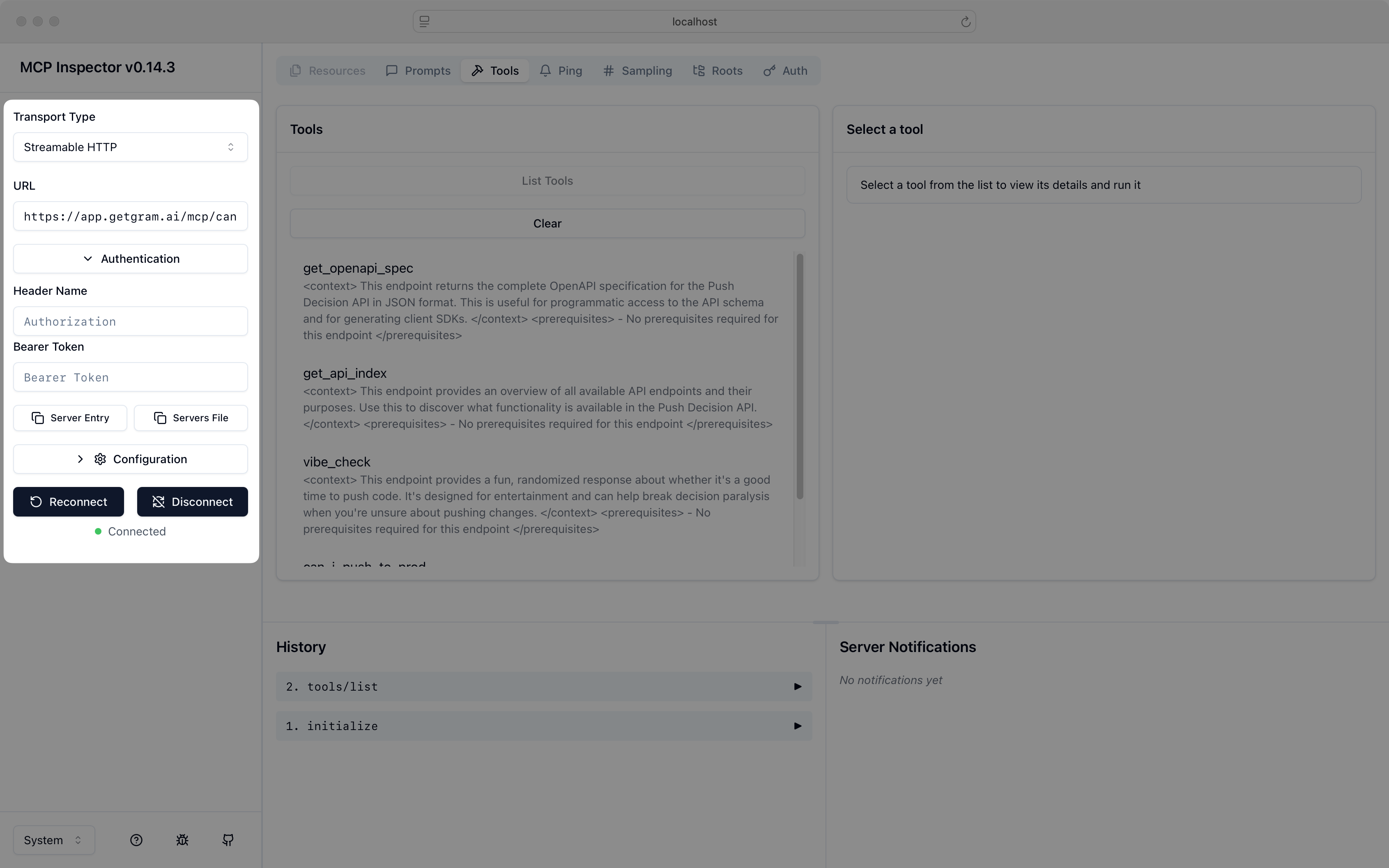
Use the Inspector to verify that your MCP server responds correctly before integrating it with your Vercel AI SDK application.
Debug tool discovery
Section titled “Debug tool discovery”You can debug which tools are available from your MCP server:
// Create HTTP transport for Gram MCP serverconst httpTransport = new StreamableHTTPClientTransport( new URL('https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod'));
const mcpClient = await createMCPClient({ transport: httpTransport,});
const tools = await mcpClient.tools();
// List all available toolsconsole.log('Available tools:');Object.entries(tools).forEach(([name, tool]) => { console.log(`- ${name}: ${tool.description}`); console.log(` Input schema: ${JSON.stringify(tool.inputSchema)}`);});
await mcpClient.close();Environment setup
Section titled “Environment setup”Ensure your environment variables are properly configured:
# .env fileOPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-api-key-hereGRAM_API_KEY=your-gram-api-key-here # For authenticated serversThen load them in your application:
import dotenv from 'dotenv';dotenv.config();What’s next
Section titled “What’s next”You now have the Vercel AI SDK connected to your Gram-hosted MCP server, giving your AI applications access to your custom APIs and tools, and giving you the flexibility to use any AI provider.
The Vercel AI SDK’s provider-agnostic approach means you can switch between OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and other providers while keeping the same MCP tool integration.
Ready to build your own MCP server? Try Gram today and see how easy it is to turn any API into agent-ready tools that work with the Vercel AI SDK and all major AI providers.