Using Cline with Gram-hosted MCP servers
Cline is a VS Code extension that embeds autonomous coding agents directly in your editor. Once installed, the extension has full read-write access to your open workspace, letting you chat with the agent, generate code, run tests, and refactor files within your editor.
When paired with Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers, you can connect Cline to your APIs, databases, and infrastructure services, granting it contextual access to your tools and data.
This guide shows you how to connect Cline to a Gram-hosted MCP server using Taskmaster, a full-stack CRUD application for task and project management. Taskmaster includes a web UI for managing projects and tasks, a built-in HTTP API, OAuth 2.0 authentication, and a Neon PostgreSQL database for storing data. Try the demo app to see it in action.
You’ll learn how to set up the connection, test it, and use natural language to manage tasks, projects, and workflows through Cline.
Find the full code and OpenAPI document in the Taskmaster repository.
Prerequisites
Section titled “Prerequisites”To follow this tutorial, you need:
- A Gram account
- A VS Code editor or any other VS Code fork such as Cursor or VSCodium
- The Cline VS Code extension installed
- A paid Cline subscription or an API key from an LLM provider supported by Cline (such as Anthropic or OpenAI)
Creating an MCP server
Section titled “Creating an MCP server”Before connecting Cline to a Taskmaster MCP server, you first need to create one. Follow our guide to creating a Taskmaster MCP server.
Connecting Cline to your Gram-hosted MCP server
Section titled “Connecting Cline to your Gram-hosted MCP server”Now let’s connect Cline to your Taskmaster MCP server.
Cline uses a configuration file to manage MCP servers.
To add a server to Cline, open the Cline panel in VS Code, click the MCP Servers icon in the Cline chat interface, and select the Remote Servers tab. Click Edit Configuration to open the cline_mcp_settings.json file.
Add your Taskmaster MCP server configuration.
-
For Pass-through Authentication, the configuration looks like this:
{"mcpServers": {"GramTaskmaster": {"command": "npx","args": ["mcp-remote","https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/your-taskmaster-slug","--header","MCP-TASKMASTER-API-KEY:<your-key-here>"]}}} -
For a Managed Authentication server, the configuration looks like:
{"mcpServers": {"GramTaskmaster": {"command": "npx","args": ["mcp-remote","https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/your-taskmaster-slug","--header","Authorization: ${GRAM_KEY}"],"env": {"GRAM_KEY": "Bearer <your-gram-api-key>"}}}}
Replace your-taskmaster-slug with the actual slug from your Taskmaster MCP server configuration and <your-gram-api-key> with your Gram API key.
Save the configuration, and your MCP server should show up in Cline’s server list under the Installed tab.
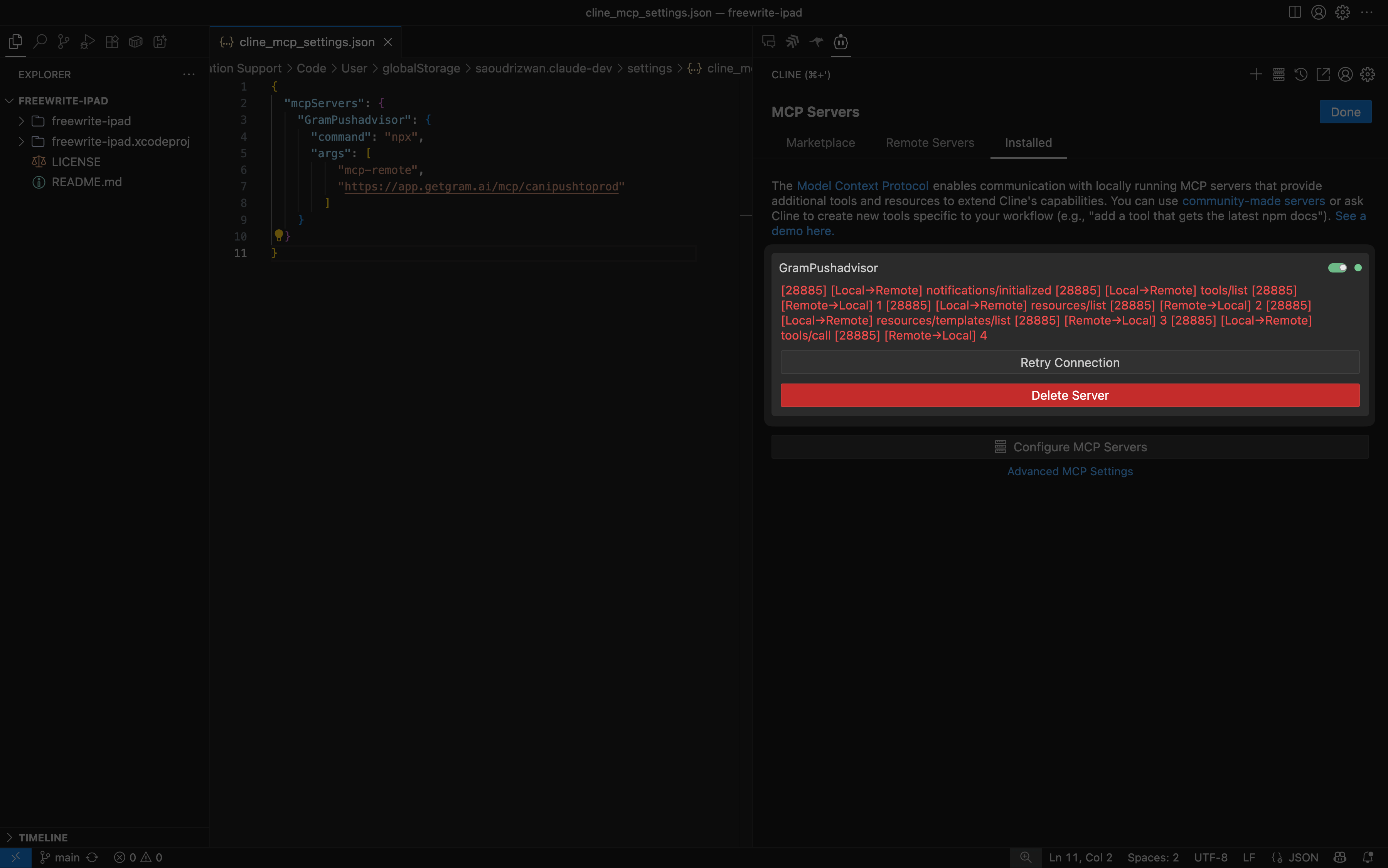
Testing the connection
Section titled “Testing the connection”Now test the connection by creating a task.
Ask Cline to do something like, “List my projects.”
Cline will use the getProjects tool to get a list of your projects. Before making the API call, it will ask for your permission to use the tool:
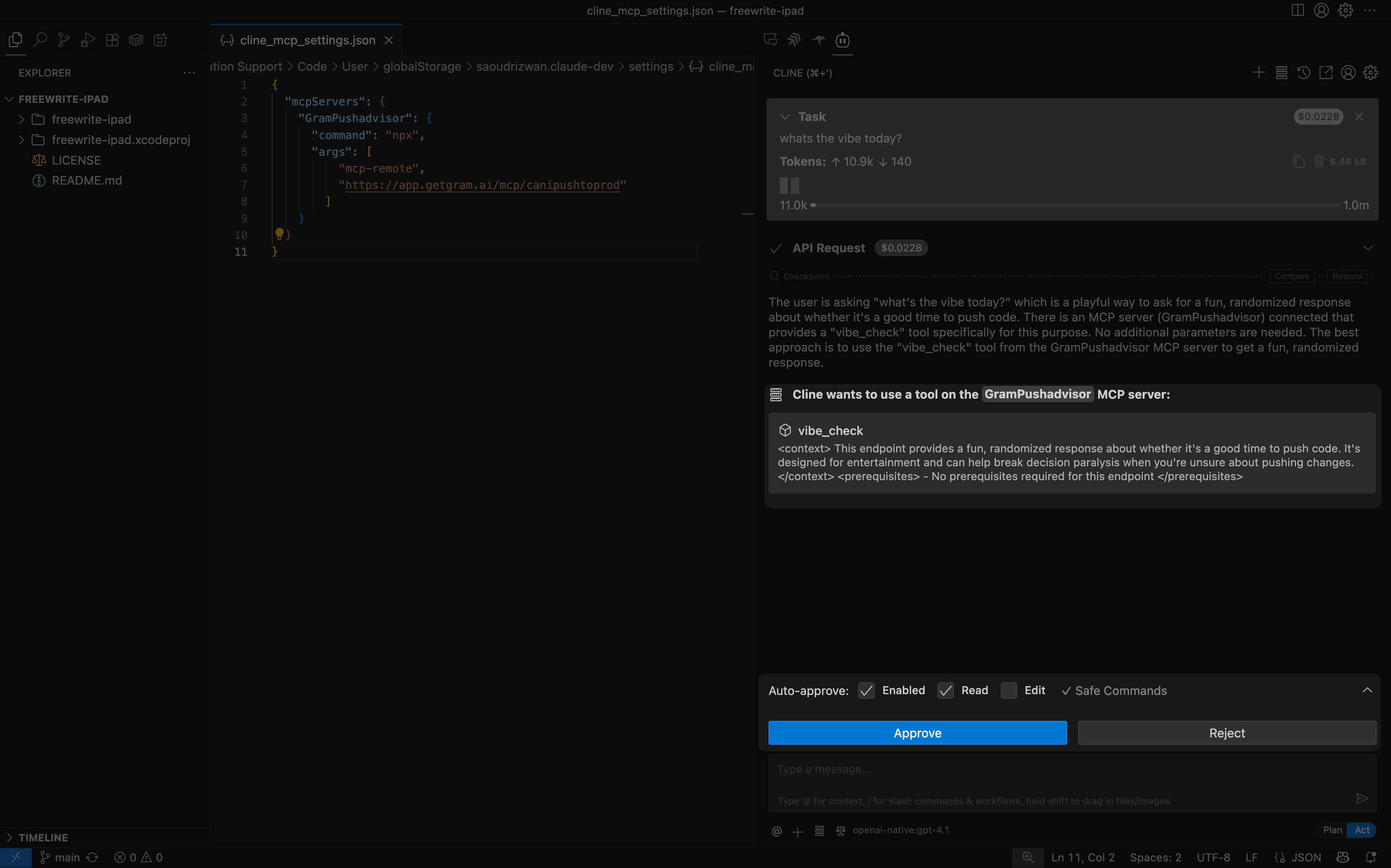
You can approve the tool call once or select Auto-approve to always allow this tool and skip future confirmation prompts. Once approved, Cline will make the API call and respond with the tool call results.
Troubleshooting
Section titled “Troubleshooting”Let’s go through some common issues and how to fix them.
Server not found
Section titled “Server not found”If Cline can’t find your server:
- Check that the MCP server configuration is correct and matches the configuration from Gram.
- Verify that the MCP server is listed in Cline’s Installed tab in the MCP Servers dialog.
- Ensure the
npxcommand is available (reinstall Node.js if needed). - Try restarting VS Code after making configuration changes.
Connection issues
Section titled “Connection issues”If you’re having trouble connecting to the MCP server:
- Verify the MCP server URL is correct in your configuration.
- Check that the API behind the MCP server is reachable from your machine.
- Try restarting VS Code after making configuration changes.
Authentication errors
Section titled “Authentication errors”If you’re using an authenticated server and getting authentication errors:
- Verify your Gram API key in the dashboard under Settings -> API Keys.
- Ensure the API key is correctly formatted with the
Bearerprefix. - Check that the
GRAM_KEYenvironment variable is properly set in your configuration.
Tools not appearing
Section titled “Tools not appearing”If the tools aren’t showing up in Cline:
- Test the MCP server in the Gram Playground first to ensure it’s working.
- Check that the toolset includes the tools you expect to use.
- Verify the environment is correctly configured with the required variables.
- Look for any error messages in Cline’s output panel or logs.
What’s next
Section titled “What’s next”Ready to build your own MCP server? Try Gram today and see how easy it is to turn any API into agent-ready tools that work across all your development environments.